The dividing line between the physical and the virtual world continues to blur. What has been viewed up until now as fantastic science fiction-that is, immersive digital experiences perfectly merged into reality-is rapidly becoming true. As technology develops, we find ourselves at the cusp of two of the most powerful tools foreseen so far: Virtual Reality and Mixed Reality. They are changing the ways in which we work, play, and connect in ways unimaginable. From gaming and education to health and business, these are the next frontier that will reshape the future of human interaction in fundamental ways.
Understanding Virtual and Mixed Reality
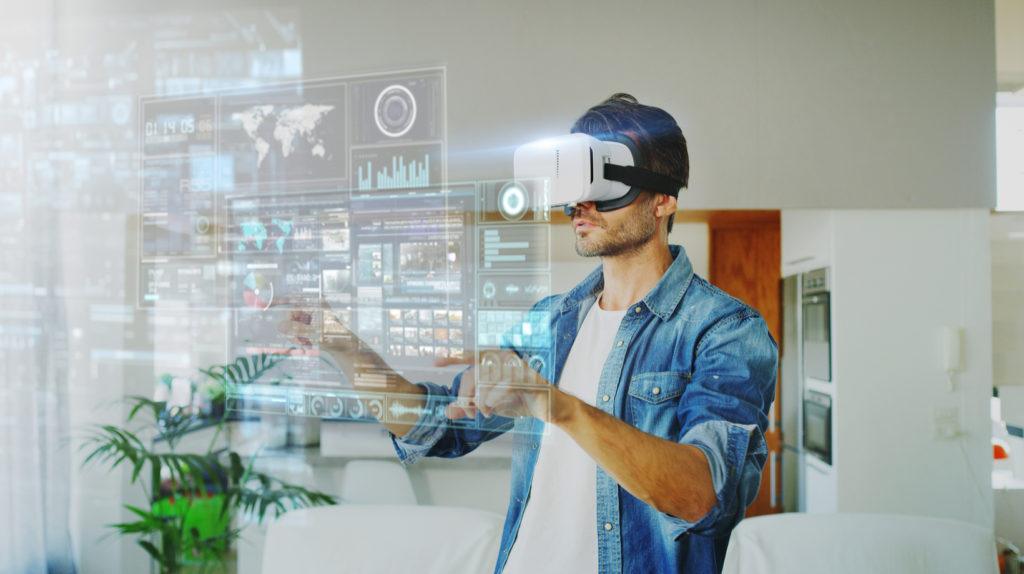
It uses headsets, like Meta Quest 3 and HTC Vive, to completely put the user inside a virtual environment. It supplants the real world with a computer-created world, giving users the ability to be immersed in highly realistic simulations, from outer space exploration to attending a virtual concert, or even training for a medical procedure.
Mixed reality is taking it even further. The platform bridges the physical and digital worlds, enabling real and virtual objects to interact in real time. Devices such as Microsoft HoloLens and Apple Vision Pro would display digital information to users superimposed on their physical surroundings. Just imagine reading emails as they float in the middle of the room, creating 3D models directly on your desk, getting a display of directions while walking down the street-that’s what mixed reality promises.
Industrial Applications
The potential of VR and MR goes beyond entertainment. It simulates going on a field trip around historical landmarks or even conducting science experiments without leaving the classroom. Medical professionals use VR in training surgeons and managing pain; MR helps visualize anatomy for doctors in real procedures.
Where virtual and mixed reality technologies are changing how collaboration has traditionally been done in the corporate world, teams now meet up in virtual offices, sharing ideas in 3D and simulating real-life scenarios for training. Other tech giants like Microsoft, Apple, and Meta are investing money in the innovations, seeing them as a future of remote work and digital communication.
These tools also have considerable benefits related to the industries of real estate and architecture. Architects use MR to project virtual blueprints onto physical spaces, while clients can virtually walk through buildings before the groundbreaking. Travel and hospitality are also embracing VR tours as users are allowed to preview destinations in 360-degree environments.

Challenges and Future Prospects
But with all the promise, a few obstacles stand in the way of VR and MR gaining widespread use: high costs, hardware limitations, and accessibility. Continuous wear also creates conditions for potential motion sickness or visual discomfort for some users. Yet, these issues should be overcome in the near future with ongoing innovations in lightweight design, 5G connectivity, and artificial intelligence. A report by PwC estimated that the XR industry, in which VR, MR, and AR fit, could add up to $1.5 trillion to the global economy by 2030. As devices go down in price and content becomes varied, it is likely that immersive technology will be as everyday as smartphones.
Concluding Points
The digital frontier is fast expanding from virtual to mixed reality. These technologies are more than entertainment; they change how we learn, work, and experience our world. As VR and MR continue to evolve, the boundary between imagination and reality will be smaller, opening up new ways of seeing, creating, and connecting. The future of technology does not lie behind the screen but around us, shaping a world where the virtual and real blend perfectly.